Functional Mushrooms: What are they?

For thousands of years, cultures around the globe have harnessed the unique properties of certain fungi for traditional medicinal purposes. Unlike the familiar mushroom varieties that we commonly find on our grocery store shelves, these ‘functional mushrooms’ are revered for their potential benefits and therapeutic properties.
Deeply rooted in tradition, functional mushrooms have a rich history in traditional Asian and Ayurvedic medicines where their use spans millennia. These remarkable fungi were prised for their ability to support overall health and certain varieties, such as Lion’s Mane, Reishi and Cordyceps, were chosen for their unique capabilities.
One of the main reasons why these mushrooms are thought to have been so popular in traditional practices is due to their rich composition of nutritional and bioactive compounds. These include polysaccharides, beta-glucans, triterpenes, antioxidants and many more, which are believed to contribute to a range of potential health benefits such as immune system support and adaptogenic capabilities.
A Rise in Popularity
In more recent years, functional mushrooms have experienced a global rise in popularity. This is likely due to several key factors:
- Shifting focus towards healthier living: People are increasingly seeking natural health solutions, leading to a greater exploration of natural remedies like functional mushrooms.
- Advancements in scientific research: Modern science is actively investigating the potential health benefits of these fungi, which will hopefully shed more light on their properties and potential benefits.
- Enhanced accessibility: Once considered rare, functional mushrooms are now widely available in convenient forms like powder and capsule supplements, teas and even coffees. This increased accessibility, often at affordable prices, makes them easier to incorporate into daily routines.
While there are many different varieties available, there are three trending functional mushrooms that have taken centre stage in the wellness arena:
Lion's Mane
Lion's Mane (Hericium erinaceus) has a unique and distinct appearance with cascading white spines, resembling a lion's mane or giant pom-poms. Native to East Asia, it has a long history in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Legend has it that Buddhist monks used it during meditation, believing it enhanced their mental clarity and focus.
More recently, Lion's mane has surged in popularity due to similar anecdotal reports of cognitive benefits shared across social media and online communities. While scientific research into its potential benefits is still in its early stages, initial findings are showing promise. Studies suggest that Lion's mane's unique compounds, hericenones and erinacines, which may stimulate the production of nerve growth factor, which plays a crucial role in nerve cell function and could potentially influence focus, memory, and overall cognitive health.
Reishi
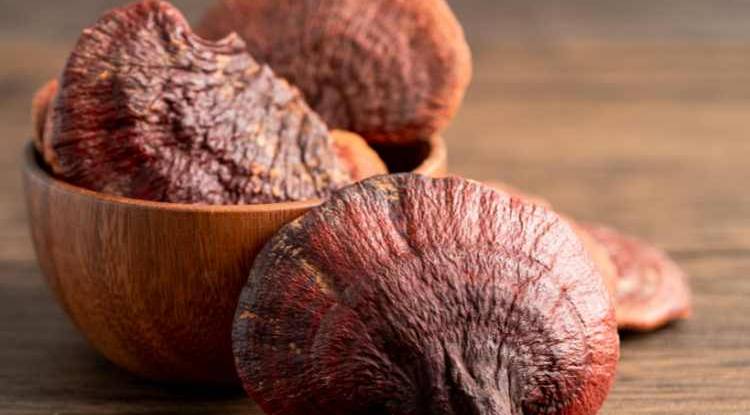
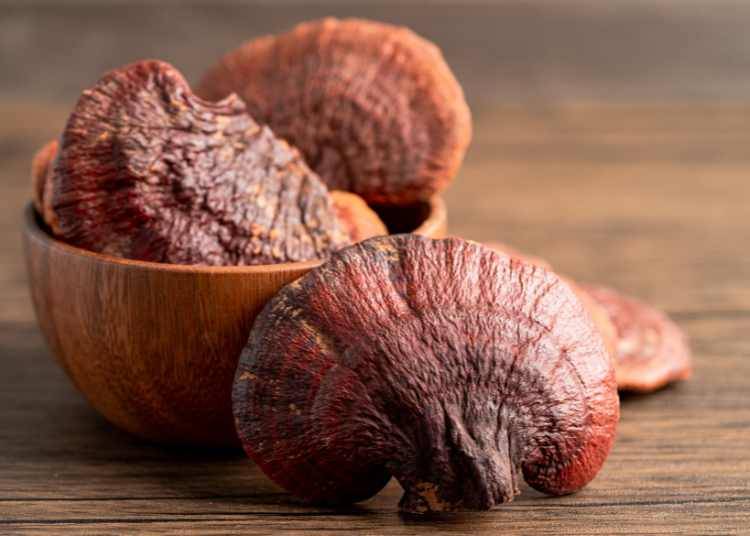
Reishi mushrooms (Ganoderma lucidum) hold a prominent place in traditional Asian medicine, often referred to as the "Mushroom of Immortality". Found throughout Asia on hardwood trees, these reddish-brown, kidney-shaped fungi are being studied for their potential to support the immune system. Initial research suggests that compounds like polysaccharides and triterpenoids may enhance white blood cell activity. They also possess antioxidant properties, which may help to protect cells against damage from free radicals.
Beyond immune support, Reishi is attracting scientific interest in other areas. Early research suggests Reishi may play a role in lowering cholesterol and hold potential adaptogenic properties, which could help the body adapt to stress and improve sleep quality. However, more studies are needed in order to substantiate these claims.
Cordyceps
Cordyceps (cordyceps sinensis) is a remarkable parasitic fungus found in the high mountain regions of China, it establishes a unique relationship with certain caterpillars, eventually growing out of its host. Due to its rarity and praise in traditional Chinese medicine, Cordyceps has been valued for centuries, believed to boost energy levels and enhance physical stamina.
Researchers are delving into the potential health benefits of Cordyceps. One area of exploration focuses on its possible influence on oxygen utilisation during exercise. If further studies substantiate this claim, Cordyceps could potentially contribute to improved endurance. Traditional use also suggests Cordyceps may support vitality and reduce fatigue. However, further investigation is necessary to understand the mechanisms behind these claims.
Summary
With their rich history in traditional medicine, functional mushrooms are experiencing a resurgence in popularity. Their unique composition of bioactive compounds like polysaccharides and antioxidants is believed to offer a range of potential health benefits. Modern scientific research is actively exploring these possibilities, focusing on areas like immune system support, cognitive function, and physical endurance in varieties like Lion's Mane, Reishi, and Cordyceps. While initial findings are promising, more studies are needed to fully understand their effectiveness. However, the increased accessibility of these mushrooms in convenient, supplement forms makes them an intriguing option for those seeking natural approaches to well-being. As research continues to bridge the gap between ancient wisdom and modern science, functional mushrooms offer an exciting frontier in holistic health.
References:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7826851/
https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/functional-mushroom-market-report
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24266378/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5987239/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6240259/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6017764/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20804368/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15857210/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4684115/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92757/
https://web.archive.org/web/20201114085403id_/
https://www.chemijournal.com/archives/2020/vol8issue5/PartAK/8-5-415-267.pdf
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8998036/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10384337/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18758067/
Note: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice.

 Sam
Sam